- This course has passed.
Healthcare Hazard Control and Safety Management
October 7, 2024 @ 9:00 am - October 11, 2024 @ 3:00 pm
KD 1950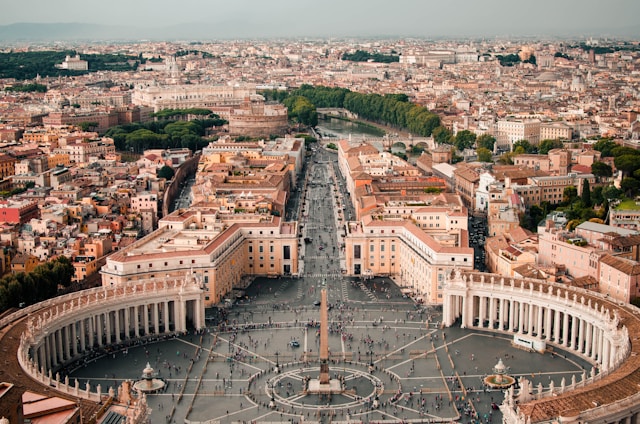
INTRODUCTION
Health and Safety within the Healthcare sector can too often become a balancing act between providing top-quality care to your patients while ensuring the health and safety of your employees and others. This doesn’t need to be a choice of one without the other. A well-designed and implemented safety management system can ensure you deliver high-quality healthcare without compromising your workforce’s health or safety.
OBJECTIVES
At the end of this Healthcare Hazard Control & Safety Management training course, you will learn to:
•Appreciate the significant legal duties for healthcare provision
•Understand the significant hazards and risks in healthcare provision
•Develop the skills to manage health and safety in line with other core Healthcare activities
•Understand risk perception and effective hazard control in healthcare
•Appreciate the importance of monitoring success for continuous improvement
COURSE OUTLINE
DAY 1
•Healthcare Management
•Legislation for health and safety in healthcare
•Developing and sustaining an effective safety management system
•The bridge between clinical and non-clinical risks
•Risk assessments and risk registers
DAY 2
•Hazards, Risks, and Controls within Healthcare – Part 1
•A hospital-acquired infection (HAI) – hazards and controls
•Sharps and needle stick management
•Cleaning, sterilisation, and decontamination
•Control of exposure to hazardous substances (including biological agents)
•Laboratory safety
DAY 3
•Hazards, Risks, and Controls within Healthcare – Part 2
•Exposure to ionising radiation, its measurement, and control
•Waste management – clinical and non-clinical
•Musculoskeletal injuries and ill-health – hazards and controls
•Stress – HSE Stress Management Standards
•Health assessment and health surveillance
DAY 4
•Maintaining a Safe Healthcare Environment
•The role and importance of facilities management
•Medical gasses
•Legislation
DAY 5
•Sustaining Safety Excellence
•Measuring performance in a meaningful way
•Active and reactive monitoring systems for healthcare safety
•Accident reporting and investigation (including the importance of near-miss reporting)